dnoiseNET - A Deep CNN for MRI Image Denoising
Improving performance without compromising quantitative metrics.
This project proposes a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) for MRI denoising that integrates residual learning and skip connections to achieve improved noise suppression without compromising clinically-relevant quantitative metrics.
Overview
In MRI, there exists an inherent trade-off between field strength, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), spatial resolution, and scan time. Achieving higher resolution often requires longer scan times and/or reduced SNR, both of which are undesirable in clinical practice. Traditional denoising methods can help improve SNR but may inadvertently alter important quantitative metrics used for diagnosis. This project introduces dnoiseNET, a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) designed to effectively denoise MRI images while preserving critical quantitative information.
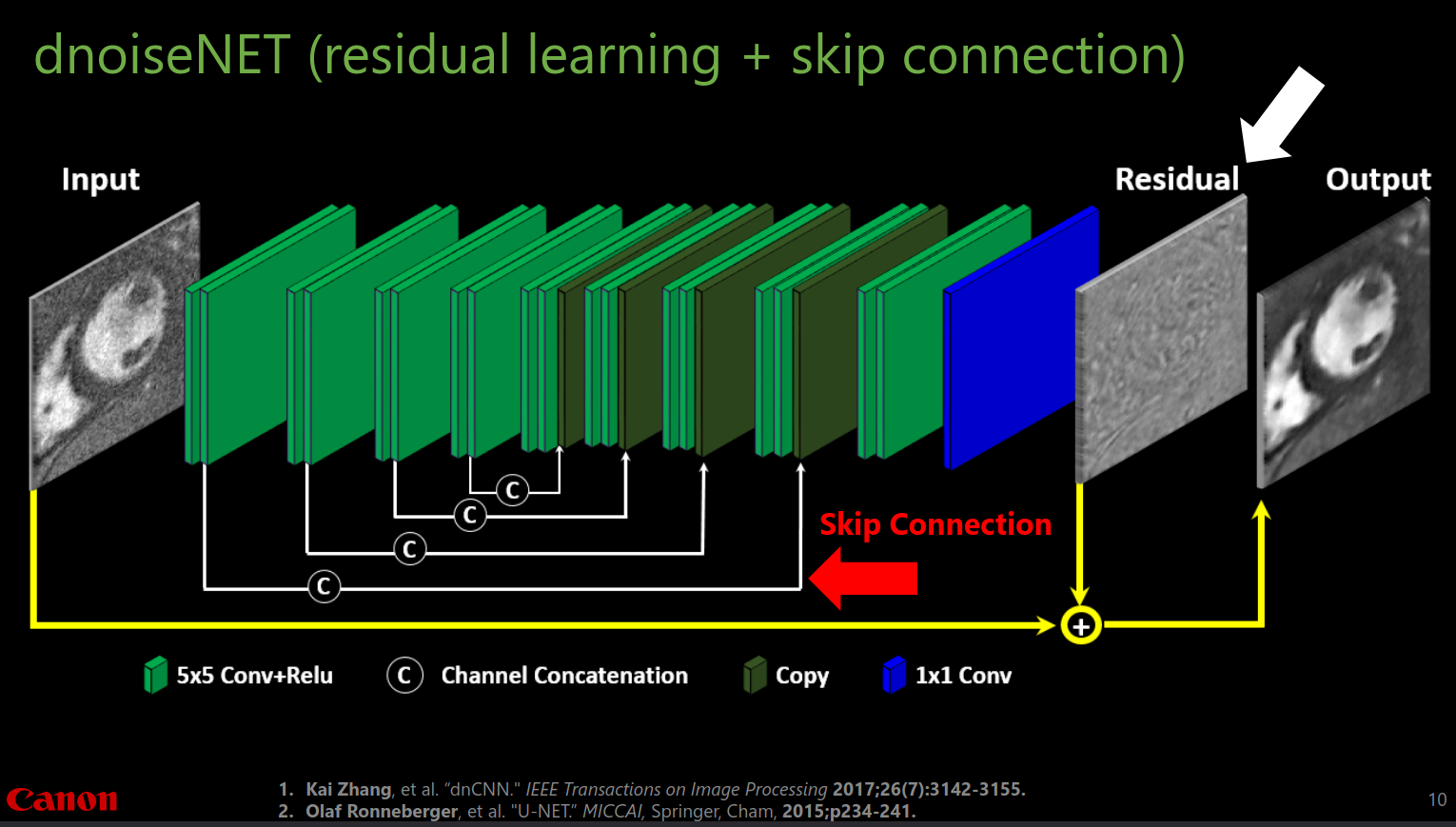
dnoiseNET: A Deep CNN for MRI Image Denoising
dnoiseNET incorporates residual learning and skip connections proposed in dnCNN (Zhang et al., 2017) and U-Net (Ronneberger et al., 2015), respectively, to enhance denoising performance:
- Residual Learning: Instead of directly predicting the denoised image, dnoiseNET learns to predict the noise component present in the input image. This approach allows the network to focus on learning the noise characteristics, making it easier to recover the underlying clean image.
- Skip Connections: These connections allow the network to bypass certain layers, enabling the flow of information from earlier layers to later layers. This helps in preserving important image details and mitigating the vanishing gradient problem.
See the conference talk’s slides for more details.
Conference talk
- HP Do, et al. "dnoiseNET: Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Image Denoising." The ISMRM & SCMR Co-Provided Workshop on the Emerging Role of Machine Learning in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Seattle, Feb 2019. SLIDES-PDF
Get future posts delivered to your inbox.