Accuracy, Uncertainty, and Adaptability of Automatic Myocardial ASL Segmentation using Deep CNN
The proposed deep CNN is designed for medical imaging, providing accurate segmentation while quantifying uncertainty and allowing control over false-positive and false-negative rates.
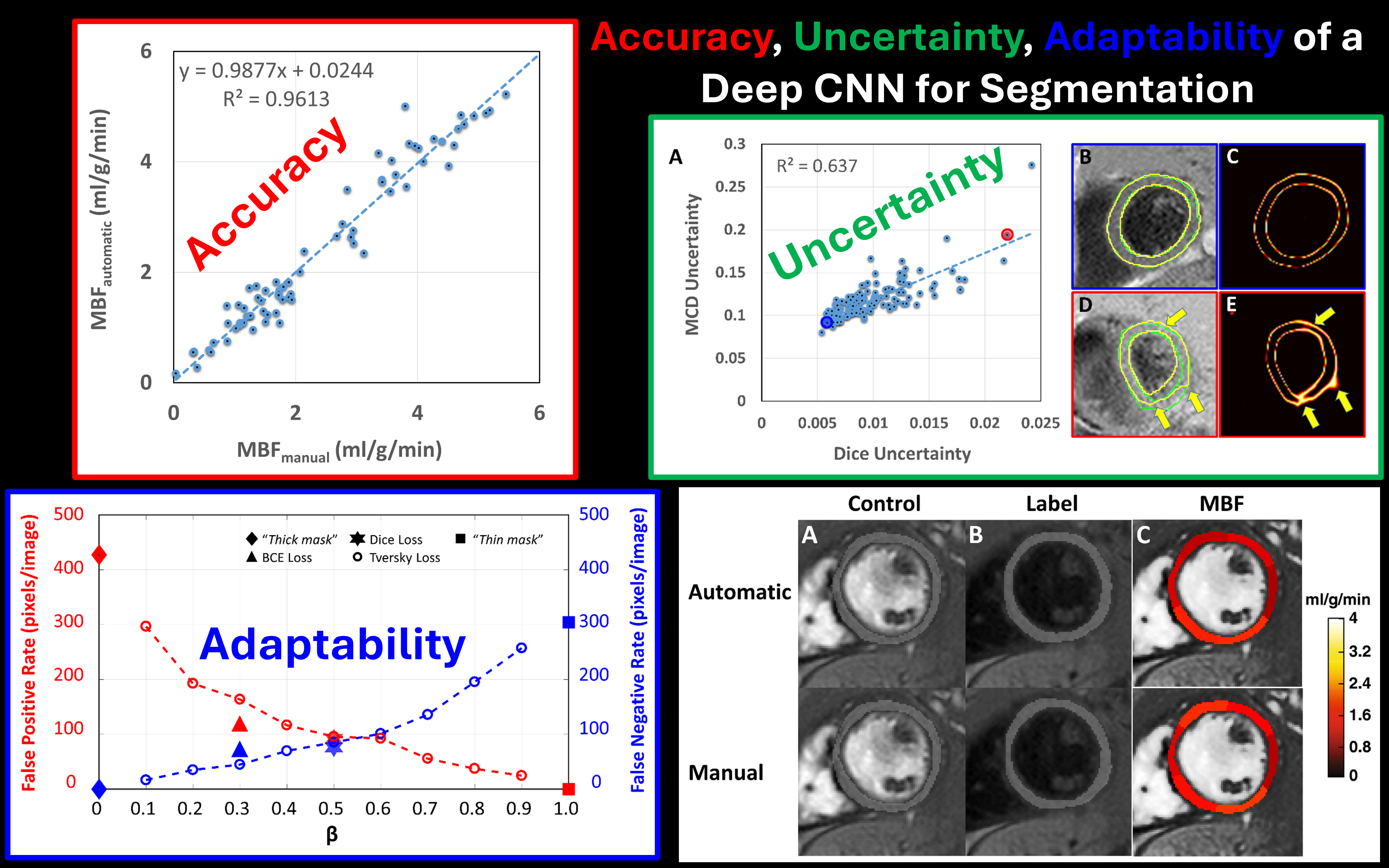
Cardiac arterial spin-labeled MRI (Cardiac ASL) is a radiation-free, noninvasive, quantitative imaging technique that measures myocardial blood flow without the use of exogenous contrast agents. However, Cardiac ASL suffers from intrinsically low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), which limits reliable pixel-wise analysis. As a result, perfusion quantification is typically performed using segmental analysis based on the American Heart Association (AHA) 17-segment model of the myocardium. This approach requires manual segmentation of the myocardium, which is tedious, time-consuming, and operator dependent.
The goal of this project is to develop an automatic myocardial segmentation method using a deep convolutional neural network (CNN). Given the safety-critical nature of medical imaging applications, we aim to address not only segmentation accuracy but also estimation of segmentation uncertainty, enabling users to identify cases that may require manual review or intervention.
Furthermore, the myocardium is anatomically adjacent to the endocardial blood pool and epicardial fat, both of which can contaminate myocardial perfusion measurements. In this context, false-positive segmentation errors are more detrimental than false negatives. Commonly used loss functions such as the Dice loss weight false positives and false negatives equally and therefore do not reflect this clinical asymmetry. To address this, we adopt the Tversky loss function, which allows explicit control over the relative weighting of false positives and false negatives to better align the optimization objective with clinical priorities.
Conference Talk:
- HP Do, et al. "Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Segmentation of Myocardial ASL Short-Axis Data: Accuracy, Uncertainty, and Adaptability." The ISMRM Workshop on Machine Learning, Part II, Washington D.C., Oct 2018. SLIDES-PDF VIDEO-YouTube
Journal paper: